Textbook for Operation and Maintenance Engineer of Power and Environment Discipline of Data Center - Basic Knowledge of Circuit - Potential and Voltage
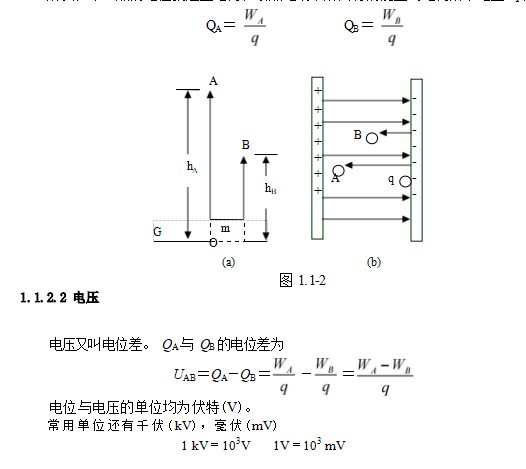
potential
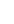
Figure 1.1-2(
a) Where G is the horizon, M is an iron block with a mass of m. Now, lift the iron block from horizon O to point A with an external force, and then the iron block has energy WA=mghA, where g is the acceleration of gravity. In order to distinguish it from electric energy, it is customarily called potential energy. If M is lifted to point B from the horizon, the potential energy of the iron block at point B is WB=mghB. The iron blocks with the same mass M are respectively lifted to hA and hB by external force, and the energy difference between them is WA-WB = mghA - mghB = mg (hA - hB). Now introduce the concept of potential. Figure 1.1-2 (b) shows a uniform electric field. Q is a positive charge with zero energy when it is close to the negative potential. When the external force moves q to point A, the potential energy of q at point A is QA. When the external force moves q to point B,
The potential energy of q at point B is QB.
Therefore, the potential at a certain point is the ratio of the energy of the positive charge in the electric field at that point to the charged quantity q of the charge.
Textbook for Operation and Maintenance Engineer of Power and Environment Discipline of Data Center - Basic Knowledge of Circuit - Potential and Voltage





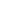

 Home
Home